User Guide/Real Time Analyser: Difference between revisions
From STX Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
(Changing from heading to semi-colon/colon formatting) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[File:rta_parameters_dialog.png]] | [[File:rta_parameters_dialog.png]] | ||
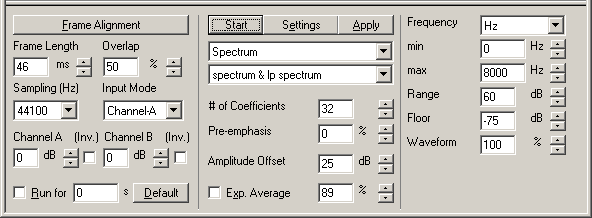
;Frame Alignment:The Frame Alignment sets the Frame Length (see below) to the value of the next highest power of two (in samples). This means that optimal frequency resolution can be obtained without loss of computational speed. | |||
The Frame Alignment sets the Frame Length (see below) to the value of the next highest power of two (in samples). This means that optimal frequency resolution can be obtained without loss of computational speed. | ;Frame Length:The frame length in milliseconds (ms). There is a minimum frame length of 5ms. | ||
;Overlap:The overlap (frame shift) in percent between frames. The value can be between 0 and 95. | |||
The frame length in milliseconds (ms). There is a minimum frame length of 5ms. | ;Sampling (Hz):The sampling rate in Hertz at which the input signal should be sampled. Note that the lower the sampling rate, the smaller the frequency scale can be (i.e. the maximum frequency is the srate/2). | ||
;Input Mode:The input mode defines how the input signal is displayed. | |||
The overlap (frame shift) in percent between frames. The value can be between 0 and 95. | ;Channel A / Channel B:Gain in decibels (dB) for channels A and B | ||
;(Inv.):Invert the signal (multiply signal with -1) | |||
The sampling rate in Hertz at which the input signal should be sampled. Note that the lower the sampling rate, the smaller the frequency scale can be (i.e. the maximum frequency is the srate/2). | ;Run for:Check the checkbox to activate the Run For feature. You can run the Real-Time Analyser for a specific number of seconds before it automatically stops. A value of 0 means run forever. | ||
;Default:The button Default sets the Run For edit box to the length of the time axis of the Real-Time Analyser display. | |||
The input mode defines how the input signal is displayed. | ;Start/Stop:Start the analyser. Once started, the button text changes to Stop. | ||
;Settings:Frame buffer, color and signal I/O settings dialog box. See the [[User Guide/Real Time Analyser/Settings Dialog for the Real-Time Analyser|Settings Dialog]] for the Real-Time Analyser for more details. | |||
Gain in decibels (dB) for channels A and B | ;Apply:Press the Apply button to apply parameter setting changes. Note that some parameter changes are applied automatically. | ||
;Spectrum/Spectrogram/Waterfall:The type of graph to display the analysis with: | |||
Invert the signal (multiply signal with -1) | |||
Check the checkbox to activate the Run For feature. You can run the Real-Time Analyser for a specific number of seconds before it automatically stops. A value of 0 means run forever. | |||
The button Default sets the Run For edit box to the length of the time axis of the Real-Time Analyser display. | |||
Start the analyser. Once started, the button text changes to Stop. | |||
Frame buffer, color and signal I/O settings dialog box. See the [[User Guide/Real Time Analyser/Settings Dialog for the Real-Time Analyser|Settings Dialog]] for the Real-Time Analyser for more details. | |||
Press the Apply button to apply parameter setting changes. Note that some parameter changes are applied automatically. | |||
The type of graph to display the analysis with: | |||
There are a number of different analysis methods available in the Real-Time Analyser. The Spectrum graph display can also display a combination of two methods. | There are a number of different analysis methods available in the Real-Time Analyser. The Spectrum graph display can also display a combination of two methods. | ||
;Method: spectrum:Computes an FFT amplitude spectrum | |||
Computes an FFT amplitude spectrum | ;Method: cp smoothed spectrum:Computes the averaged cepstrum smoothed amplitude spectrum, via the inverse transform of the lowpass filtered cepstrum. | ||
;Method: lp spectrum:Compute the averaged transfer function (amplitude) using the LPC auto-correlation method. | |||
Computes the averaged cepstrum smoothed amplitude spectrum, via the inverse transform of the lowpass filtered cepstrum. | ;# of Coefficients:The number of coefficients used for the computation of the cp smoothed spectrum or lp spectrum. | ||
;Pre-emphasis:Signal differentiation factor in percent. 0 to 100% are valid values. | |||
Compute the averaged transfer function (amplitude) using the LPC auto-correlation method. | ;Amplitude Offset:The amplitude offset between the two methods (only available for combined methods in the Spectrum graph). | ||
;Exp. Average:Check the checkbox to activate the exponential averaging. Values from 0 to 99% are valid. | |||
The number of coefficients used for the computation of the cp smoothed spectrum or lp spectrum. | ;Frequency:The frequency unit to use for the frequency axis. | ||
;min/max:The minimum and maximum frequency to display. Note that the validity of the values are dependant on the sampling rate. | |||
Signal differentiation factor in percent. 0 to 100% are valid values. | ;Range:The amplitude range to display. | ||
;Floor:The lowest end of the amplitude range. | |||
The amplitude offset between the two methods (only available for combined methods in the Spectrum graph). | ;Waveform:Percentage of full attenuation to display. | ||
;x-axis / y-axis:Only available if the Waterfall graph display is being used. The x-axis determines what percentage of the graph's width should be used for the x axis. Possible values are -100 to 100%. A negative value means that the x-axis is bound to the right hand side of the display. | |||
Check the checkbox to activate the exponential averaging. Values from 0 to 99% are valid. | |||
The frequency unit to use for the frequency axis. | |||
The minimum and maximum frequency to display. Note that the validity of the values are dependant on the sampling rate. | |||
The amplitude range to display. | |||
The lowest end of the amplitude range. | |||
Percentage of full attenuation to display. | |||
Only available if the Waterfall graph display is being used. The x-axis determines what percentage of the graph's width should be used for the x axis. Possible values are -100 to 100%. A negative value means that the x-axis is bound to the right hand side of the display. | |||
==Settings== | ==Settings== | ||
Open the [[User_Guide/Real_Time_Analyser/Settings_Dialog_for_the_Real-Time_Analyser|settings dialog]] to set the number of frames/samples per buffer and the graph colors. | Open the [[User_Guide/Real_Time_Analyser/Settings_Dialog_for_the_Real-Time_Analyser|settings dialog]] to set the number of frames/samples per buffer and the graph colors. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:59, 13 March 2019
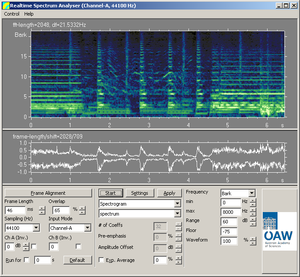
The STx Real-Time Analyser can analyse mono or stereo input from any available source on the system. Three analysis displays are implemented:
- Spectrum
- Spectrogram
- Waterfall
Parameters
The Real-Time Analyser is provides a large number of parameters for altering the analysis display.
- Frame Alignment
- The Frame Alignment sets the Frame Length (see below) to the value of the next highest power of two (in samples). This means that optimal frequency resolution can be obtained without loss of computational speed.
- Frame Length
- The frame length in milliseconds (ms). There is a minimum frame length of 5ms.
- Overlap
- The overlap (frame shift) in percent between frames. The value can be between 0 and 95.
- Sampling (Hz)
- The sampling rate in Hertz at which the input signal should be sampled. Note that the lower the sampling rate, the smaller the frequency scale can be (i.e. the maximum frequency is the srate/2).
- Input Mode
- The input mode defines how the input signal is displayed.
- Channel A / Channel B
- Gain in decibels (dB) for channels A and B
- (Inv.)
- Invert the signal (multiply signal with -1)
- Run for
- Check the checkbox to activate the Run For feature. You can run the Real-Time Analyser for a specific number of seconds before it automatically stops. A value of 0 means run forever.
- Default
- The button Default sets the Run For edit box to the length of the time axis of the Real-Time Analyser display.
- Start/Stop
- Start the analyser. Once started, the button text changes to Stop.
- Settings
- Frame buffer, color and signal I/O settings dialog box. See the Settings Dialog for the Real-Time Analyser for more details.
- Apply
- Press the Apply button to apply parameter setting changes. Note that some parameter changes are applied automatically.
- Spectrum/Spectrogram/Waterfall
- The type of graph to display the analysis with:
There are a number of different analysis methods available in the Real-Time Analyser. The Spectrum graph display can also display a combination of two methods.
- Method
- spectrum:Computes an FFT amplitude spectrum
- Method
- cp smoothed spectrum:Computes the averaged cepstrum smoothed amplitude spectrum, via the inverse transform of the lowpass filtered cepstrum.
- Method
- lp spectrum:Compute the averaged transfer function (amplitude) using the LPC auto-correlation method.
- of Coefficients
- The number of coefficients used for the computation of the cp smoothed spectrum or lp spectrum.
- Pre-emphasis
- Signal differentiation factor in percent. 0 to 100% are valid values.
- Amplitude Offset
- The amplitude offset between the two methods (only available for combined methods in the Spectrum graph).
- Exp. Average
- Check the checkbox to activate the exponential averaging. Values from 0 to 99% are valid.
- Frequency
- The frequency unit to use for the frequency axis.
- min/max
- The minimum and maximum frequency to display. Note that the validity of the values are dependant on the sampling rate.
- Range
- The amplitude range to display.
- Floor
- The lowest end of the amplitude range.
- Waveform
- Percentage of full attenuation to display.
- x-axis / y-axis
- Only available if the Waterfall graph display is being used. The x-axis determines what percentage of the graph's width should be used for the x axis. Possible values are -100 to 100%. A negative value means that the x-axis is bound to the right hand side of the display.
Settings
Open the settings dialog to set the number of frames/samples per buffer and the graph colors.
Menus
If you would like a detailed explanation of the menus / context menus, read this article.