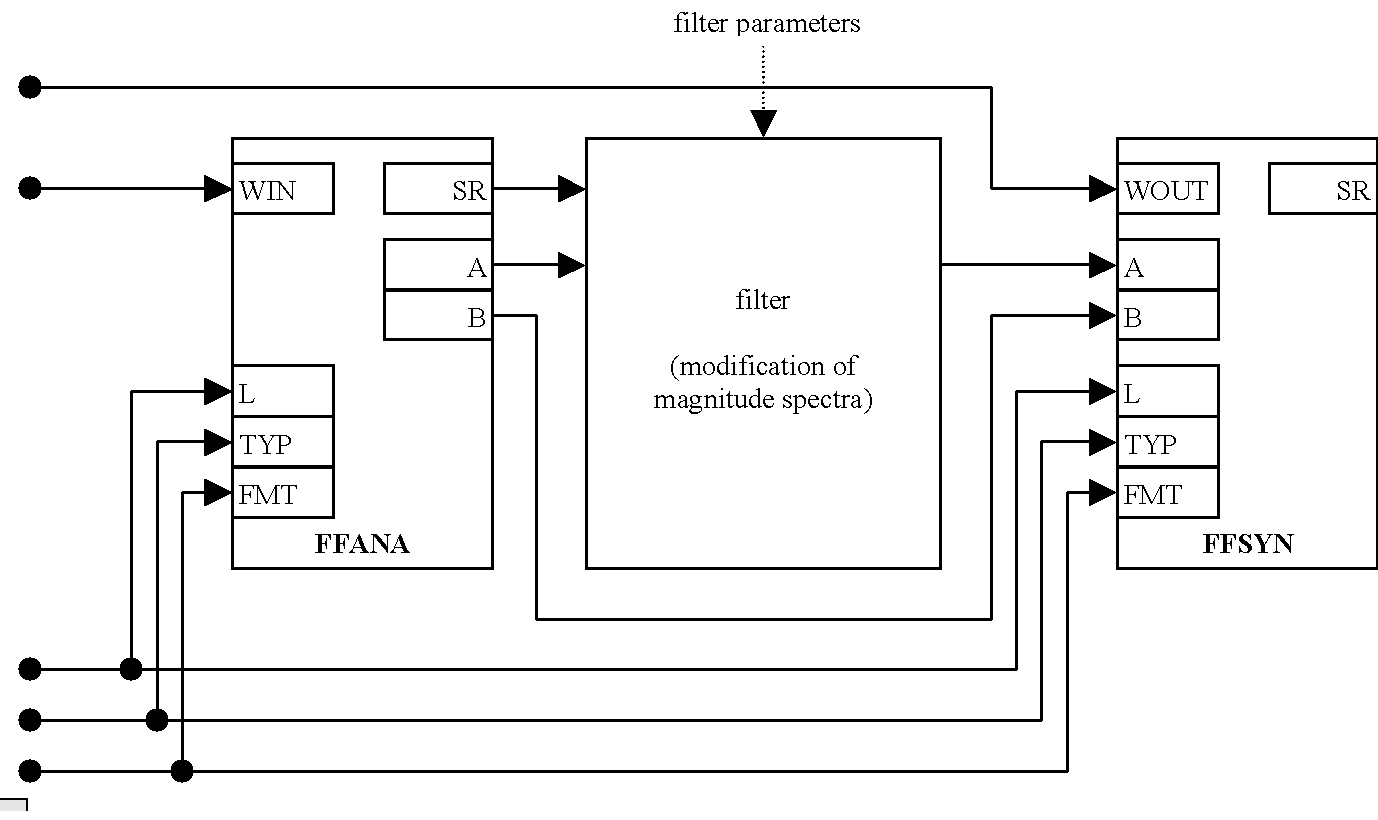
FFANA FFSYN
Contents
FFANA / FFSYN - filter I/O modules - simple Wiener filter implementation
Analyse a signal using a simple Wiener filter.
Usage:
FFANA WIN L TYPE FMT
Inputs:
- WIN
- The name of a shell wave item for signal input (mono).
- L
- The filter/frame length in samples.
- TYPE
- The analysis/resynthesis filter type. The following values are supported:
NOOVERLAP|0- a frame with 2.n samples is used for analysis, where the first half is filled with a signal frame and the 2nd half is set to 0. This method minimizes the effects (distortions) of the cyclic convolution. The input frames are not overlapped. The length of A and B is 2.(n/2+1).
HALFOVERLAP|1- the input signal is multiplied with a Hanning window and half overlapped. The length of A and B is n/2+1.
- FMT
- The format of the output spectrum The following values are supported:
COMPLEX|0- A is the real part and B the imaginary part of the complex spectrum.
MAGNITUDE|1- A is the magnitude spectrum and B the phase spectrum.
POWER|2- A is the power spectrum and B the phase spectrum.
Outputs:
- A
- First part of the signal spectrum (dependant on FMT).
- B
- Second part of the signal spectrum (dependant on FMT).
- SR
- The sampling rate.
Synthesise a signal using a simple Wiener filter.
Usage:
FFSYN WOUT L TYPE FMT A B
Inputs:
- WOUT
- The name of a shell wave item for the signal output (compatible to WIN).
Outputs:
none
Function:
The two atoms FFANA and FFSYN implement the analysis and re-synthesis modules for signal processing methods using the fast-convolution technique. The FFANA atom partitions the signal into frames and performs the Fourier transform. The synthesis module FFSYN uses the inverse Fourier transform and an overlap-add method to reconstruct the signal stream.
The FFT length n is set via the input L. If L is not a power of 2, the FFT length is set to the next power of 2 greater than or equal to L. The spectrum of the current frame is stored in the outputs A and B.
The source and target wave items must be mono signals with equal sampling rates and lengths. At the end of the process, the analyser atom appends zero-frames to the signal, while the synthesis-atom empties the delay buffers.
In the following example of a filter SPU, the magnitude spectrum is processed by the modification module and the phase spectrum is left untouched. For the filter/modification section any kind of stationary or adaptive process can be used.
Functional diagram of FFANA and FFSYN SPAtoms in the framework of the STx analysis/synthesis model.