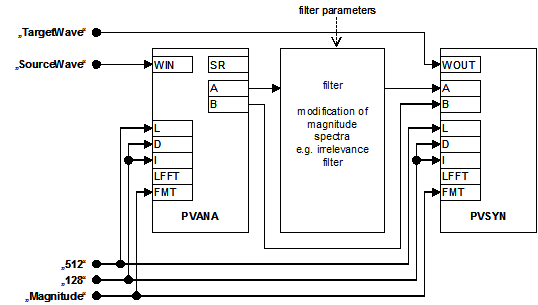
PVANA PVSYN
Contents
PVANA / PVSYN - phase vocoder I/O modules
Phase vocoder analysis.
Usage:
PVANA SIGIN L D I LFFT FMT TYPE WIN WTYPE
Inputs:
- SIGIN
- The input signal (the name of mono wave item).
- L
- The frame length in samples.
- D
- The decimation length in samples.
- I
- The interpolation length in samples
- LFFT
- The FFT length.
- FMT
- The spectrum format. The following values are supported:
0 - complex
1 - amplitude
2 - power
Note that negative amplitudes are allowed for amplitude spectrum values (FMT==1).
- TYPE
- The algorithm type - 1..amplitude thresholding.
- WIN
- The window name:
rectangle|hanning|hamming|blackman|kaiser|bartlett|taprectangle|nuttall|flattop|gaussian
- WTYPE
- The window type:
normal|dual|tight
Outputs:
- A
- The first part of the spectrum (depending on format FMT).
- B
- The second part of the spectrum (depending on the format FMT).
- SR
- The sampling rate.
Phase vocoder synthesis.
Usage:
PVSYN SIGOUT L D I LFFT FMT A B WIN WTYPE
Inputs:
- SIGOUT
- The name of the shell wave item for signal output (compatible with SIGIN).
See the above atom PVANA for a description of the other input parameters.
Outputs:
- N
- The number of frames.
- I
- -1
Function:
This atom implements the phase vocoder as published in the book "Elements of Computer Music" (R. F. Moore. Elements of Computer Music. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cli#s, NJ. USA, 1990). The spectrum format (FMT) has to be set to 1 or 2 (amplitude or power) for this atom to truly represent a phase vocoder, for only then is phase-unwrapping and differentiation done. If the spectrum format is set to 0 (complex), this atom implements a channel vocoder. It can be used as an analysis or re-synthesis module for signal time-warping and/or signal modification methods in the frequency domain.
The advantage of the phase vocoder over other analysis/re-synthesis methods is the time and phase synchronicity of the input and output signals. For time-warping, the factor between the input and output timescales is defined by the ratio of the decimation to the interpolation length (D/I). If no timescale transformation should be performed, the values of D and I must be equal. In the current implementation, the "overlap-add" re-synthesis method is included, but not the "oscillator bank" method. This atom can therefore be used for time-warping, but not for frequency-warping.
Conditions for the parameters L, D and I:
L mod D = 0 and L mod I = 0 and L< LFFT
The example shows a filter circuit using PVANA/PVSYN for signal I/O. No timescale modification is performed (D=I):
Figure: Functional diagram of PVANA and PVSYN SPAtoms in the framework of the STx analysis-synthesis model.